SQL Mathematical Functions
Use SQL mathematical functions to perform business and engineering calculations. I’ll cover the commonly used functions, as you won’t many of them in day-to-day operations.
If you’re new to SQL and want to get to know more about SQL Function right now, then read Introduction to SQL Server Built-In Functions.
All the examples for this lesson are based on Microsoft SQL Server Management Studio and the AdventureWorks2012 database. Get a head start learning SQL. Download my free guide Getting Started Using SQL Server.
Introduction to SQL Server’s Mathematical Functions
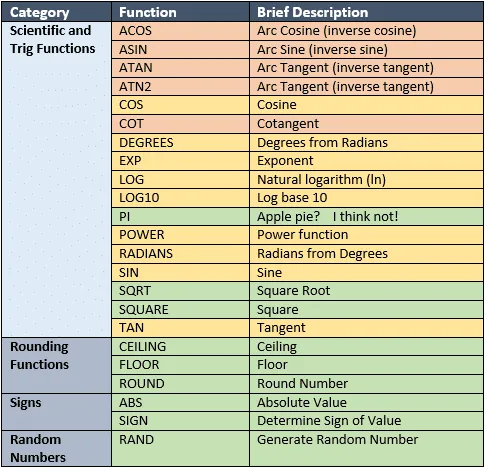
There are many SQL mathematical functions for you to use. I categorize them as:
- Scientific and Trig Functions
- Rounding Functions
- Signs
- Random Numbers
The SQL MSDN page is a great reference. If you want to dig deep into functions, it is your go to place.
Rather than reiterate that material, let’s focus on the functions commonly used in business.
I put together a table of functions. It is color coded. The color code corresponds to the likely hood you’ll used a particular function within business: Green are most likely used, and red less so.
OK – SpaceX will use some of the red ones, but hey, they’re rocket scientists!
This isn’t a strict scale, and all functions are awesome (I’m an engineer and love math), but I wanted a way to help you winnow down the field to those most relevant.
Here is my attempt:
Latest Posts
-
SQL CEILING Function (Transact SQL)
The SQL CEILING function returns the smallest integer value greater than or equal to the input value. Description The CEILING function evaluates the right side of the decimal value and returns an integer value that is least greater than or equal to the input value. CEILING is another SQL function for approximating numerical values like…
-
SQL FLOOR Function (Transact SQL)
The SQL FLOOR function returns the largest integer that is smaller or equal to the input expression. Description The FLOOR function helps for approximating numeric values. It rounds the numeric expression to the value that is the largest number less than or equal to the input number. SQL FLOOR Usage Notes The FLOOR function takes…
-
SQL RAND Function (Transact SQL)
The SQL RAND function generates a random number between the range of 0 and 1. The number can be greater than equal to zero but less than one. Description The RAND function gives a completely random number if no seed value is specified. The RAND function produces a repetitive random number for all the successive…
-
SQL ROUND Function (Transact SQL)
The SQL ROUND function rounds a numeric value up to a specified number of decimal places or precision. Description The SQL ROUND function helps to handle numeric data according to the requirements. Some other SQL functions for this purpose are CEILING, FLOOR, etc. If we do not want to display complete numeric values, we can…




