The SQL Greater Than comparison operator (>) is used to compare two values. It returns TRUE if the first value is greater than the second. If the second is greater, it returns FALSE.
You can also test for greater than or equal to by using >=.
Here are a couple of examples:
| 10 > 5 | TRUE |
| 5 > 20 | FALSE |
| 10 > 10 | FALSE |
Here is an example using the SQL greater than comparison operator to find all products whose list price is greater than $3000.
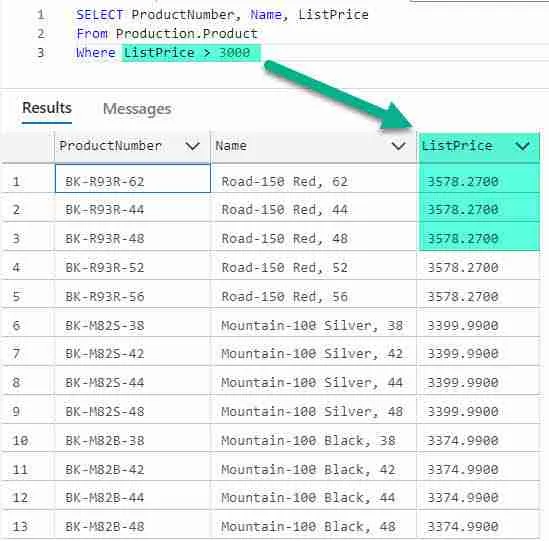
Only rows whose ListPrice is more than $3000.00 are included in the results. Try it for your self!
SQL Greater Than with Other Types
You can use the greater than comparison with other data types, such as String and DateTime.
Here we’re returning products modified after February 1st, 2014.
When working with text values, such as names and address, keep in mind your DBMS collating order. It will affect how these operators work. In simple terms the collating order is (A-Z) ascending, but you can can that!
Additional Resources
To learn more about greater than (>), check out these useful resources: