In this article you’ll learn to use the LIKE operator in your SQL. In most situations you’ll find yourself using LIKE within the WHERE clause to filter data using patterns such as all values beginning with “S.” Using this phrase allows us perform partial matches of data values and obtain answers to questions which can’t be done with conventional comparisons.
The lesson’s objectives are to:
- learn about the LIKE match condition
- understand wild cards
Important! Please follow along and do the examples in your database. If you haven’t already done so, sign up for my Guide to Getting Started with SQL Server. You get instructions on how to install the free tools and sample database.
Table of contents
SQL WHERE LIKE Pattern Matching
The LIKE match condition is used to match values fitting a specified pattern. Unlike the equals (=) comparison operator, which requires an exact match, with LIKE we can specify a pattern to partially match fields.
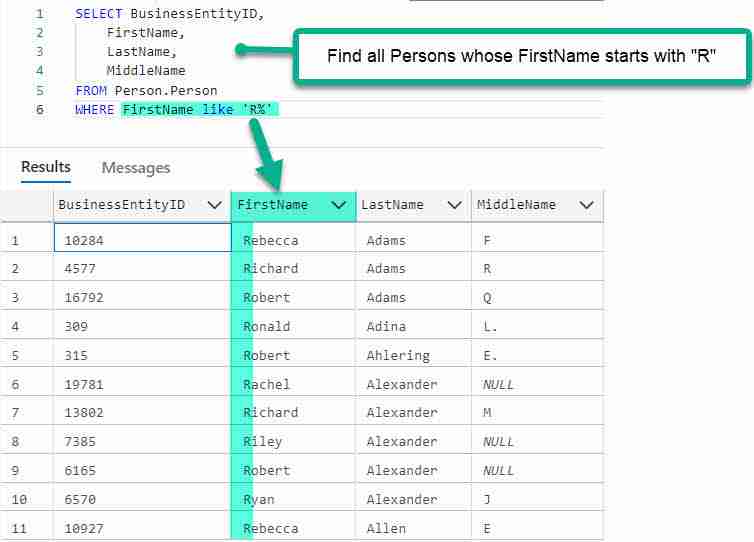
An example where clause using the LIKE condition to find all Employees whose first names start with “R” is:
SELECT BusinessEntityID,
FirstName,
LastName,
MiddleName
FROM Person.Person
WHERE FirstName like 'R%'
The big thing to see here is that we use LIKE to do the matching.
You may be wondering what is so special about that search as you could just as easily as written
WHERE FirstName >= 'R' AND FirstName < 'S'
to achieve the same result, but what about finding all names ending in the letter s? There is no easy way to use the traditional comparison operators to do this, but it’s easily handled with LIKE:
SELECT BusinessEntityID,
FirstName,
LastName,
MiddleName
FROM Person.Person
WHERE FirstName like '%s'
The ‘R%’ and ‘%s’ are patterns. Patterns are created using placeholder characters. There are several special characters used.
Commonly used SQL LIKE Wildcards
When working with LIKE you find yourself using wildcards to create the pattern matching. The most common wildcard to use are those that match any characters or exactly one character.
| Wildcard | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| % | Any string of zero or more characters | WHERE FirstName LIKE ‘G’ finds all names beginning with G. |
| _ (underscore) | A single character | WHERE FirstName LIKE ‘T_M’ finds all three letter names beginning with T and ending in M, such as Tim and Tom. |
| [] | Any single character within a range or set such as [e-i] or [efghi] | WHERE FirstName LIKE ‘T[aeiouy]%’ finds all names starting with T whose second letter is a vowel, such as Tammy. |
| [^] | Any single character not within a range or set, such as [^1-4] or [^1234] | WHERE FirstName LIKE ‘T[^aeiouy]%’ finds all names starting with T whose second letter is not a vowel, such as Thomas. |
Note: There are a couple of more wildcards you can use to specify ranges, but for now, we are going to focus on the most popular ones.
I’m getting a head of my self here, but these wildcard are trippy. So, before we get too much farther, lets show that list example’s results to visually see how it works!

Notice that the [^aeiouy] is restricting FirstName. No First Names contain vowels in the second position.
SQL Like % and _ Wilds Card Examples
Let look at the % wildcard. The pattern ‘%and%’ matches to ‘Wand‘, ‘and‘, or ‘Standard.’
To find all state abbreviations starting with the letter N, we could use the pattern ‘N%’ as this would match all values who first character is “N” and then any characters afterwards.
Yet, since state abbreviations are two characters ‘N_’ is more accurate, as this states to first match ‘N’ and then one and only one character thereafter. We can also match an anti-pattern using NOT. If you’re looking for all names that do not end in S, the clause to use is
WHERE FirstName NOT LIKE '%s'
This would match ‘Baker’, ‘Michigan’, or ‘Wolverine,’ but not ‘Sales’ or ‘Kites’
As with other clauses, LIKE comparisons can be combined with other comparisons using AND and OR.
So, to find all employees in the AdventureWorks2012 database who are managers and females, we can use the following query:
SELECT NationalIDNumber,
JobTitle,
BirthDate,
MaritalStatus,
Gender,
HireDate
FROM HumanResources.Employee
WHERE Employee.JobTitle LIKE '%manager%'
AND Employee.Gender = 'F'
Here you can see the pattern matching in action.
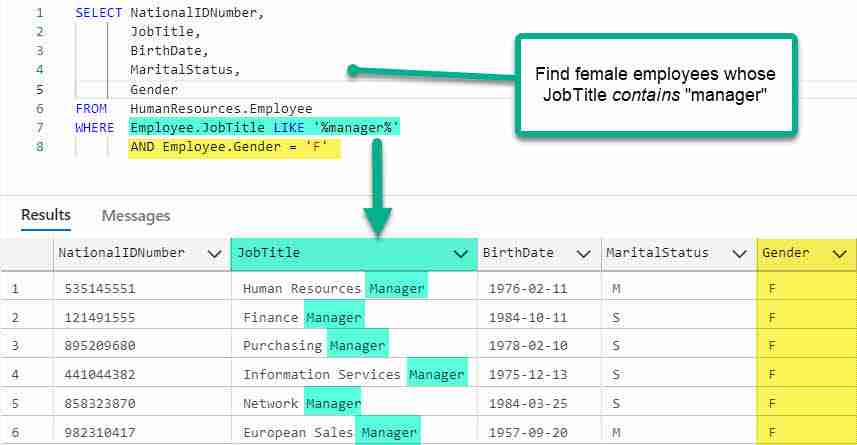
Also, check out how we combined the LIKE clause with an equality using the AND conditional operator.
Use SQL Like to Match a 1-800 Phone Number
So if you wanted to search for “1-800” phone numbers you could do a search like
WHERE PhoneNumber LIKE '%800%'
But that could match more than you bargained for as numbers such as 1-248-703-9800 could also match. So, you could refine the search to be more specific.
WHERE PhoneNumber LIKE '%(800)%'
OR PhoneNumber LIKE '%800 %'
To match numbers such as (800) 555-1212 or 1-800 555-1212; however, this could backfire, as now numbers such as 1-800-555-1212 wouldn’t match, of course you could catch this with additional match terms. The final result would be:
WHERE PhoneNumber LIKE '%(800)%'
OR PhoneNumber LIKE '%800 %'
OR PhoneNumber LIKE '%800-%'
Matching a Social Security Number
You may have a situation where you wish to retrieve all government ID’s matching the pattern of a US social security ID. In order to do this match you could use the following
WHERE GovernmentID LIKE '___-__-____'
This would match numbers such as ‘123-12-1234′, but not ’12-12-12’ If you were looking to find all ID’s that didn’t match a social security number you could write your query as:
WHERE GovernmentID NOT LIKE '___-__-____'
SQL Like Exercises
It’s important to practice! Use the sample database to answer these questions.
- Find all Employees that have marketing in their title
- Select all persons whose street address is on a drive. Hint – There are two forms of Drive: Dr. and Drive.
- Select all products whose product number’s numeric portion starts with 7. Hint – The product number’s format is AA-9999.
Learn More about SQL WHERE LIKE
Looking to learn more? Check out these articles to learn more about the LIKE clause and other interesting SQL topics:




Leave a Reply