This article is inspired by a series of questions that one of my readers, Nan, recently sent me regarding SQL DISTINCT, TOP, and ORDER BY.
All the examples for this lesson are based on Microsoft SQL Server Management Studio and the AdventureWorks2012 database. You can get started using these free tools using my Guide Getting Started Using SQL Server.
How do the SQL Top and Distinct SELECT modifiers Work Together to Produce Results?
Nan’s Original Question
Here is the question that Nan originally sent me:
I’m a bit confused about SELECT DISTINCT and SELECT. For example,
SELECT DISTINCT TOP 10 FirstName,
LastName
FROM Person.Person
ORDER BY LastName
Is this looking at distinct first names? Distinct combined first and last names? How do we distinguish between the columns used for the distinct evaluation and columns we just want to show in the output?
What about
Select Distinct TOP 10 LastName,
FirstName + ' ' + LastName AS FullName
FROM Person.Person
ORDER BY LastName
I thought everyone would like to know the answer so I create a blog post.
SQL DISTINCT and TOP – Which is First?
Let’s look at the first statement who purpose is to return a unique list of fist and last names.
SELECT DISTINCT TOP 10 FirstName,
LastName
FROM Person.Person
ORDER BY LastName;
TOP 10 will return the first ten items from the ordered set, and SQL DISTINCT will remove any duplicates. The question is which happens first?
- Is the table sorted by LastName and the top ten items taken, and then duplicate name removed?
- Or are the duplicates removed, and then the items sorted and the top ten items displayed?
More About SQL DISTINCT
Before we answer this question keep in mind that DISTINCT operates on all columns and expressions in the SELECT clause. So, in this case, the statement will return distinct rows for FirstName and LastName.
Unfortunately there is no direct way to use DISTINCT on one set of fields and display others. Once you add columns to the SELECT statement they become under the influence of the DISTINCT operator. I say direct, as you could get a distinct list, and then use a INNER JOIN to pull in other columns. There are dangers to doing that though, as the join may reintroduce duplicates.
Add TOP to DISTINCT
Adding a TOP clause to DISTINCT is interesting. I wasn’t sure what would happen, but I did some experimenting with the AdventureWorks database and found that the order of processing goes something like so:
- Select DISTINCT Values from Table and order
- Select the TOP x rows from the results in step 1 and display.
If you want to try this yourself start with
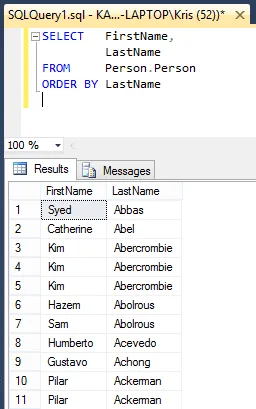
SELECT FirstName,
LastName
FROM Person.Person
ORDER BY LastName
And notice the results. Keep track of “Kim Ambercombie.” Notice how there are three entries for her name.
Now run
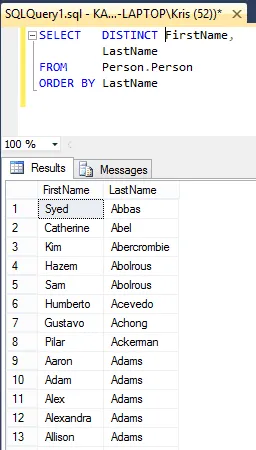
SELECT DISTINCT FirstName,
LastName
FROM Person.Person
ORDER BY LastName
And you’ll see that “Kim Ambercombine” is shown only once.
Then run
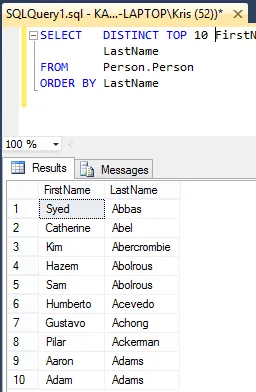
SELECT DISTINCT TOP 10 FirstName,
LastName
FROM Person.Person
ORDER BY LastName
And you’ll see it returns first 10 unique first and last names as sorted by LastName.
Use the Query Plan To Confirm Order
If you’re wondering which happens first, the SQL DISTINCT or TOP 10 operations, then compare the results from the last two queries.
Notice that the query “DISTINCT TOP 10” includes the first 10 rows from the query from the “DISTINCT” query.
From this we know a DISTINCT list is first created, and then the TOP 10 items returned.
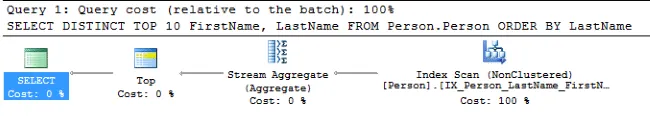
You can also confirm this by showing the query plan. To do so, select Query -> Include Actual Query Plan from the menu before executing the query.
The “Stream Aggregate” icon is for the DISTINCT operation and “Top” for the TOP 10 one.
It may seem somewhat counterintuitive to see DISTINCT listed first within the SELECT statement. Just keep in mind SQL isn’t necessarily processed in the order a human would read it from left to right.
DISTINCT and TOP with SELECT list Expressions
The second portion of Nan’s question related to how expressions are treated with the DISTINCT operator.
Expressions are treated the same as column regarding DISTINCT and TOP. Let’s start with a select statement to get the first name as well as the full, which we create by appending LastName to FirstName.
Also, keep in mind, when using ORDER BY, that the ORDER BY items must appear in the select list when using Distinct. Given this I have to modify the statement presented in the original question:
SELECT DISTINCT FirstName,
FirstName + ' ' + LastName AS FullName
FROM Person.Person
ORDER BY LastName
Won’t run since LastName isn’t in the SELECT list. Yes, it is part of an expression in the select list, but its not there on its own. It is valid to order by FullName.
We’ll use this ordering in the examples below.
The statement
SELECT FirstName,
FirstName + ' ' + LastName AS FullName
FROM Person.Person
ORDER BY FirstName + ' ' + LastName
Returns 19972 rows. When we add Distinct
SELECT DISTINCT FirstName,
FirstName + ' ' + LastName AS FullName
FROM Person.Person
ORDER BY FirstName + ' ' + LastName
Then 19516 rows are returned. Finally adding Top 10, returns the first 10 distinct name combinations.
SELECT DISTINCT TOP 10 FirstName,
FirstName + ' ' + LastName AS FullName
FROM Person.Person
ORDER BY FirstName + ' ' + LastName
Try running these queries on the AdventureWork database and you see for your self the behavior is the same as we find when working exclusively with columns.




Leave a Reply