The SQL SUM function returns the total value within a table or group.
In its simplest use, SUM() totals a column for all results and returns a single value.
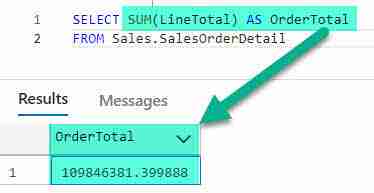
In this example the query returns the total orders for all SalesOrderDetail records
SELECT SUM(LineTotal) AS OrderTotal FROM Sales.SalesOrderDetail
You can also filter your results prior to totaling. Here the SUM() is restricted to two SalesOrders:
SELECT SUM(LineTotal) AS OrderTotal FROM Sales.SalesOrderDetail WHERE SalesOrderID in (43659, 43662)
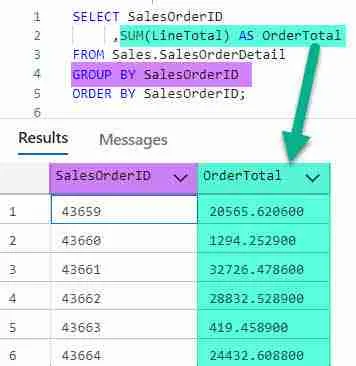
Of course it’s more fun to use SUM() when working with GROUPS! Rather than sum two sales orders, let’s return a summary of sales, by SalesOrder. To do so, we’ll use SQL SUM in conjunction with GROUP BY.
SELECT SalesOrderID, SUM(LineTotal) AS OrderTotal FROM Sales.SalesOrderDetail GROUP BY SalesOrderID ORDER BY SalesOrderID
Now that you’ve seen SUM() in actions. Let’s check out some other places you can use it!
For instance did you know you can sort by SQL SUM. Here’s the same query now ordering result by the OrderTotal:
SELECT SalesOrderID, SUM(LineTotal) AS OrderTotal FROM Sales.SalesOrderDetail GROUP BY SalesOrderID ORDER BY SUM(LineTotal)
What’s really cool about this is the data is grouped by SalesOrderID, but sorted by the total. Nifty huh?
Additional SQL SUM Resources
To learn more, check out these useful resources:




Leave a Reply